
Cloud Banking: the Future of Banking, or What Banking Sector will look like in 2030
Cloud computing is moving to the forefront as a focus for IT leaders, C-suite executives, and board members. In its 2021 survey, The Economist Business Intelligence Unit found that 72% of executives in the banking sector are convinced that implementing cloud solutions into their products will help in achieving their business goals. The movement towards the cloud has already started with such large financial services organizations as Deutsche Bank, Wells Fargo, Goldman Sachs, and HSBC announcing deals with AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure back in 2020.
In this article, we will discuss how financial services will look like with the cloud in the future, and how the cloud can become a catalyst for your business transformation—and a potential game-changer in the highly competitive financial sector.
What is Cloud-Based Banking
The bank of 2030 will look very different from today. Facing changing consumer expectations, advanced technologies, and alternative business models, banks need to start putting strategies in place now to help them prepare for this future. For example, cloud banking is moving to the forefront as a focus for the chief information officer, C-suite executives, and board members.
Cloud-based banking refers to deploying and managing banking infrastructure to control core banking operations and financial services without dedicated physical servers.
How Does Cloud Banking Work
Microsoft, Google, Azure, and other cloud service providers handle the complex cloud infrastructure and allow banks to use it for specified fees. Some of the typical cloud service models include:
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)—delivers a fully-fledged banking infrastructure that handles business operations and software integrations. It provides the highest level of flexibility and management control over the IT resources and is most similar to existing IT resources that many IT departments and developers are familiar with today.
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)—provides cloud-based banking software for accounting, invoicing, customer relationship management, and other business priorities. Choosing SaaS, you only need to think about how you’ll use that particular piece of software. The most popular software as a service apps are Google Docs, Microsoft Office 365, Gmail, Jira, and WordPress. SaaS applications often offer advanced settings and development environment options. Social networks also work according to the SaaS model.
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)—offers a cloud-based banking platform for application and database development. With PaaS, you don’t need to worry about resource procurement, capacity planning, software maintenance, or any of the other undifferentiated heavy lifting involved in running your app. Salesforce Heroku, Google App Engine, VMware Cloud Foundry, and IBM Bluemix are popular examples of cloud platforms such as PaaS.
In addition, cloud hosting (also known as cloud computing deployment models) is also divided into 3 types.
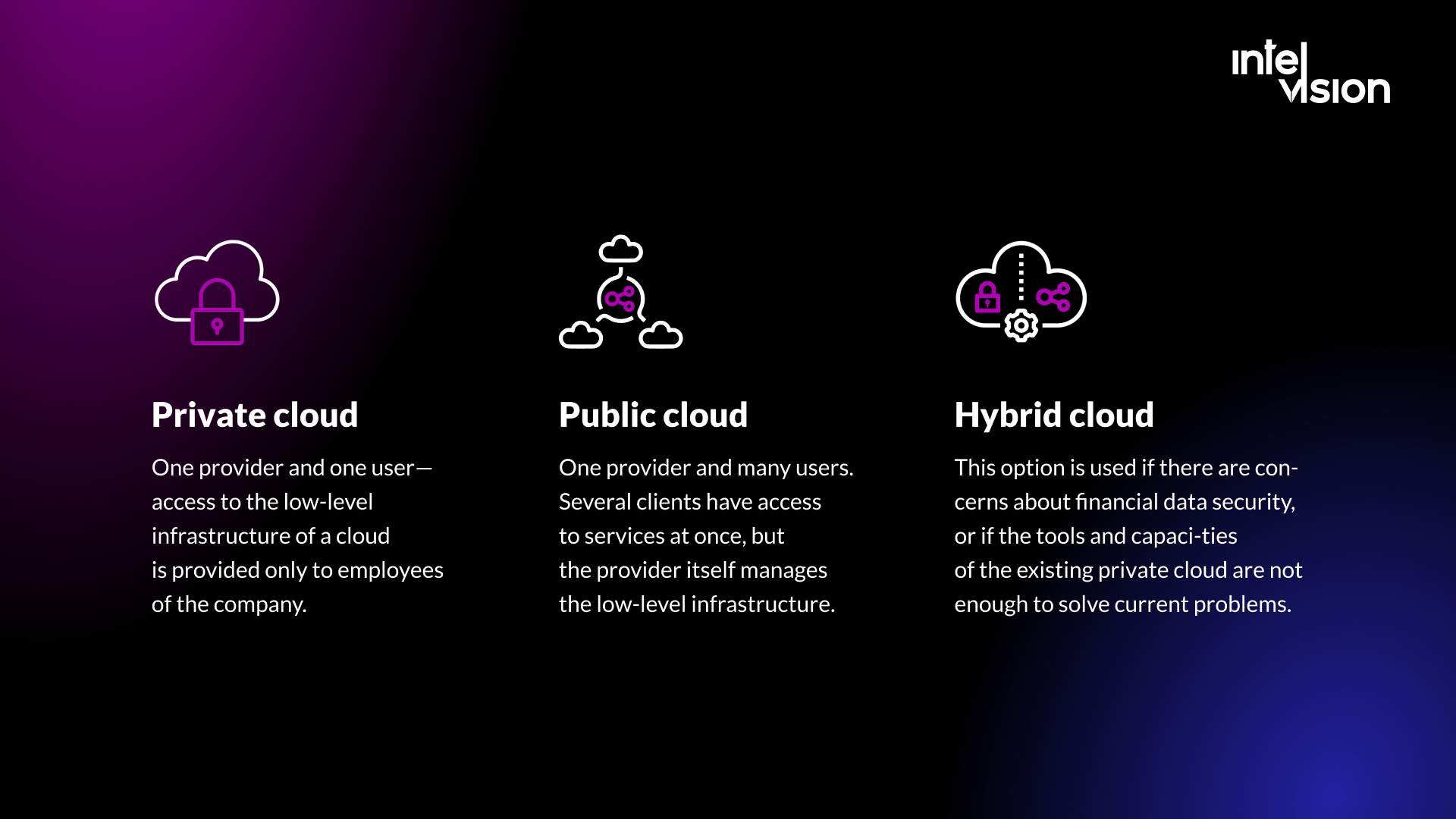
Private cloud
One provider and one user—access to the low-level infrastructure of a cloud is provided only to employees of the company.
Public cloud
One provider and many users. Several clients have access to services at once, but the provider itself manages the low-level infrastructure.
Hybrid cloud
This option is used if there are concerns about financial data security, or if the tools and capacities of the existing private cloud are not enough to solve current problems.
Advantages of Cloud-Based Banking
About 95% of US and European banks already use cloud solutions in one form or another, while an increase in investment by 30% in this area is noted. The largest players have long transferred their servers to cloud infrastructure. For example, PayPal is one of them. Cloud banking startups quickly scale and capture the market share of more traditional banking organizations. Large banks see this threat, so they also invest in advanced technologies.
Let’s look through the critical sources of value enabled by applying cloud technology:
Synchronize the enterprise
- Better integration of business units through sharing data, driving integrated decisions, and moving more quickly to solve customer problems.
- Creating common, connected data sets; enabling deeper, more sophisticated insights and analytics; enhancing collaboration through new shared platforms and tools, and increasing the speed of decisions.
Build resilient operations
- Enhance financial institutions’ overall resilience to respond more quickly—physical outages, disruption, etc.
Enhance IT security
- Cloud providers have extreme security standards. Environments can be as secure or more secure than on-premises, implemented correctly, with skilled and trained security.
Last but not least, for banks and financial organizations, the issue of customer service in automatic mode is a tool to reduce risks. It becomes less profitable to maintain your infrastructure from software and your servers—updates, staffing, and troubleshooting. These issues generate additional costs. Storing, processing and interbank exchange of customer financial data can be safer, cheaper, and faster thanks to cloud banking.
Key Trends and Approaches in the Banking Sector
Firstly, the banking cloud is becoming more popular in the past few years, and both private and public clouds have been used. The analytical agency Gartner reports that in 2020, 4% of commercial CBS were installed through a private cloud, another 2.5%—through a public cloud. In the case of fintech startups, the technology began to dominate at all. Almost ¾ of new developers of banking decisions use cloud services for deployment.
Secondly, the popularity of a hybrid banking cloud is growing among large banks. High safety requirements are pushed by companies to store the most sensitive data and place critical infrastructure in a private cloud within the financial institution. Additional tools and affiliate services can be connected using a public cloud.
Thirdly, the widespread use of cloud exceptional financial services significantly increased the role of the API in app development and integration with various systems. More and more organizations can correctly build architecture using API ships for interaction.
What's Next?
The role of cloud technologies in banking services and products will grow every year. In addition, there will be a reduction in software costs for employees of banks and financial institutions. According to the Gartner analytical agency, more than 75% of organizations will begin to use cloud technologies by 2025, to optimize the costs of working tools and provide access to the necessary services through a cloud.
With banking cloud technologies, we will have a significant increase in the number of payment systems as a service. The main advantage of this approach is that the time to withdraw products to the market (Time-to-Market) is significantly reduced.
The Last But Not Least…
The benefits of banking on the cloud are increasingly evident, such as enhanced customer satisfaction, faster product development, and more agile systems scalability. The move to the cloud can also introduce important capabilities to access and mine data more prolifically as well as provide opportunities for significant cost reductions through automation.
For rival banks, clouds have become part of the technological development strategy. An example is the American Capital One Bank, which reduced from 8 to 3 the number of data centers thanks to banking cloud technologies.
Bank of America (BOA) spends up to $10 billion per year on technological solutions, including chatbots, mobile apps, and developing its cloud. One of the largest banks in the US began to create it in 2013. At the same time, BOA deliberately abandoned the services of third-party companies such as Amazon, Microsoft, and Google. The development of its cloud saves Bank of America $2 billion annually. BOA innovations didn’t go unnoticed by the banking community and banking on cloud— Global Finance put them in first place in the annual ranking of world banks, including for exceptional financial services and technological banking solutions.
If you need help implementing on-premise or cloud-based digital banking solutions for your financial institution, contact us right away. Our financial software development services will help you build a cloud banking product within a short timeframe. Plus, we’ve partnered with hundreds of companies over the past years to boost their development capabilities. Reach out to discuss your cloud banking product needs.











![$portfolio_img_mobile['title'] $portfolio_img_mobile['alt']](https://intelvision.pro/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/Fortuna-project-cover-mobile-262x350.png)









